14
Dispatch → Account → Military
AQ-20B Renegade
AQ-20B Renegade |
|||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Role | Uninhabited combat | ||||||||||||||||||
National origin | |||||||||||||||||||
Manufacturers | Aerodyne Inc. | ||||||||||||||||||
First flight | 2 June 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
Introduction | 18 August 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
Status | In service | ||||||||||||||||||
Primary users | See Operators | ||||||||||||||||||
Produced | 2013-present | ||||||||||||||||||
Number built | ?,000+, plus | ||||||||||||||||||
Unit cost | US$40 million | ||||||||||||||||||
Variants | AQ-20B | ||||||||||||||||||
Developed from | OA-20A Havoc II | ||||||||||||||||||
The AQ-20B "Renegade" is a carrier-capable Group 4 uninhabited aerial system (UAS)/Tier III medium-altitude, long-endurance (MALE) tactical uninhabited combat aerial vehicle (TUCAV) developed from the airframe of the out-of-service crewed OA-20A "Havoc II" twin-engine, pusher prop, observation and attack aircraft. It is designed for low speed/low altitude operations, being highly manoeuvrable in all modes of flight, having a low accoustic signature for stealthy battlefield surveillance, high airworthiness and robust airframe for high survivability from enemy ground fire. It is capable of human-supervised semi-autonomous, all-weather, day/night operations. It possesses a long loiter endurance and wide-area sensor coverage to perform persistent intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR) missions over the battlefield; the payload and responsiveness to provide immediate lethal strike against high value and time critical targets and support distributed operations with on-call close-air support (CAS); and defensive electronics to ensure high survivability in contested airspace. The AQ-20B is self-flying using a human-in-the-loop system for mission planning and execution with autonomous flight functions to reduce operator workload including active ‘sense and avoid’ (SAA) systems to allow safe operation in mixed manned/unmanned environments. It has robust fault-tolerant avionics and high-throughput open architecture mission computers. it uses processors and algorithms for sensor fusion to quickly detect, identify, locate and track fixed, relocatable, and mobile targets, and jam resistant high data rate STANAG 7085 compliant datalink and low-rate detalink to allow real-time on- and off-board sensor exchange and target cueing. Advanced cognitive decision aids give operators the situational awareness and positive air vehicle control necessary to authorize munitions release confidently.
The AQ-20B is developed from a single-seat, twin-engine, pusher configuration of increased fuel and power efficiency with the engine and prop at the rear to allow unobstructed visibililty from the front and easy access by ground crew to the engines and underwing pylon stations. The aircraft was designed to be simple and robust allowing it to be serviced and operated from bases with limited facilities near battle areas. It is certified to STANAG 4671 uninhabited combat aerial vehicle (UAV) airworthiness standards featuring a low-observable airframe, self-sealing fuel tanks and multiply-redundant aircraft systems. These include a fault tollerant digital flight control system with dual redundant i.e., primary and backup digital flight computers, triplex redundant digital fly-by-wire (DFBW) system using fibre-optic linkages, and dual redundant electromechanical flight control actuators. The aircraft is a low-wing monoplane with large un-swept high aspect ratio low taper wings offering high lift for short take-off and landing (STOL) performance and increased endurance to loiter on target for extended periods. Leading and trailing edge flaps provide aileron boost for quick roll response for pulling high g manoeuvres and resistance to stalls and spins at low speed. Wing-folding mechanisms at the mid-wing point reduce aircraft spotting size with armanent carried on eight underwing store stations, two inboard (one wet and one dry) and two outboard of the fold on each wing, for a maximum of 8,000 lb or 4 tons of ordnance including bombs, missiles, torpedoes, rockets, podded guns and cannons, and other stores e.g., fuel tanks, and refuelling, sensor and electronic warfare pods. The empennage consists of a Y-tail with mixed rudder and elevator controls consisting a single ventral stabiliser stressed to withstand ground impact and twin canted ruddervators of high control effectiveness for superior handling. The pressurised cockpit with armoured 'bathtub' and bubble canopy of the crewed OA-20A is fully omitted. The area is smoothly faired over improving laminar flow to reduce drag with a bandpass frequency selective surface that forms a conformal radome for a dual mode high-resolution synthetic aperture radar/moving target indicator (SAR/MTI) sensor of high atmospheric attenatuation in all weather conditions. A universal aerial refueling receptacle slipway installation (UARRSI) is located forward. The belly mounted cannon and stores stations of the OA-20A are also omitted replaced by a gyrostabilised sensor ball turret with electro-optic/infrared (EO/IR) payload containing daylight and low-light level TV and forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras for difficult target detection, multi-target tracking, real-time imagery intelligence and battle damage assessment, and eye safe dual mode laser ranger finder/target designator (LRF/LTD) for precision aimpoint targeting. The radio frequency and opto-electronic sensors offer a 360° field of regard for wide-area high-altitude over-the-horizon reconnaissance and surveillance. Propulsion is mounted in the rear fuselage arranged in a low-drag pusher-prop configuration consisting twin contra-rotating scimitar propellers. They are driven by twin independent turboshaft engines with integral starter-generators and full authority digital engine controls (FADEC) that supply power via a 3.2:1 ratio combining/reduction gearbox with separate clutches to cushion torsional load changes. The engine intakes are large air scoops forward of both wing roots. An uneven blade count of one six-blade and one five-blade prop lowers vibration and therefore acoustic signature to a level equivalent to a single prop. Engines and props can be selectively disengaged for economical single-engine cruise performance and increased loiter endurance, or to automatically compensate for a power failure during take-off or landing. All fuel is located away from the propulsion system in self-sealing armoured wing tanks. Anti-icing systems include pneumatic de-icing boots fitted to to all wing and tail leading edges with no propeller de-icing required as any blade ice formation is prevented by the eflux of the two turboshaft engines. The airframe is constructed as a graphite/epoxy composite semi-monocoque fatigue, fail-safe, and damage tollerant structure that offers a minimum service life of 20 years. It comprises graphite frames and longerons bonded to composite honeycomb panels to form the fuselage, and multi-spar bonded stressed skin fail-safe structures forming the wings and tails. Polycarbonate armouring resistant to blast, flame and 23 mm cannon hits protects the engines, fuel tanks and avionics bays, and fragment protection of fuel lines, busbars and wiring by aramid fibre overwraps protecting from fragments. A robust, high-strength landing gear with shock absorbers and large low-pressure tyres permits operation from carrier flight decks with ski-jump ramps and using electro-magnetic aircraft launch and recovery equipment (ALRE), and from unimproved landing fields and forward-area strips, with the landing gear semi-retracted into wing nacelles to allow gear-up belly landings in an emergency.
Etoile Arcture Aerospace Forces
Etoile Arcture Maritime Forces
Royal Joseon Navy The Great state of Joseon
The Great state of Joseon
Fortress State Royal Navy Fortress State Royal Marine Corp Fortress State Ground Defence Force Animarnia
Animarnia
- used by Fleet Air Arm
National Security Forces - used by the Air Force.
Specifications (AQ-20B Block II)
Data from Aerodyne specifications.
General characteristics
Crew: 0 onboard (3 remote: Launch and Recovery Element (LRE) pilot; Mission Control Element (MCE) pilot and sensor operator)
Length: 16.36 m
Wingspan: 18.49 m
Height: 4.47 m
Wing area: ?? m²
Empty weight: 6,347 kg
Loaded weight: 13,656 kg
Max. takeoff weight: 14,336 kg
Powerplant: 2 × Powerdyne AT930 turboshaft, 1,642 kW (2,201 shp) flat rated to 1,483 kW (1,988 shp) each
Propellers: 1 × Ratier-Figeac scimitar six-bladed + five-bladed contra-rotating graphite/titanium pusher propellers
Internal fuel capacity: 4,360 kg
Wingspan, wings folded 11 m
Performance
Maximum speed:
At sea level: 375 knots
At altitude: Mach 0.58
Cruising: Mach 0.49
Combat radius: 650 km (351 nm) on internal fuel
Ferry range: 2,600 km (1,404 nm) with external fuel tanks
Endurance: 24 hours
Maximum operational altitude: 15,544 m (51,000 ft)
Service ceiling: 7,620 m (25,000 ft)
Maximum design g-load: +3.0 g to -3.0 g
Armament
Stations: 8 x under-wing hardpoints
2 wet inboard wing pylons rated @ 1,587.6 kg (3,500 lb)
2 dry middle wing pylons rated @ 1,134 kg (2,500 kg)
4 dry outboard wing pylons rated @ 453.6 kg (1,000 lb)
Stores: maximum weapon load of 3,629 kg (8,000 lbs)
Guns:
2 × M25/SUU-23/A Gun Pod with M134D Minigun six-barrel 7.62×51mm NATO Gatling machine gun or GAU-19/A (GECAL 50) three-barrel 12.7×99mm NATO Gatling machine gun
Rockets:
4 × LAU-61C/A (19-tube, Hydra-70 2.75 inch FFAR (Folding Fin Aerial Rocket) or AGR-20A APKWS II (Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System)) for total of 76 rockets
4 × LAU-68D/A (7-tube, Hydra-70 2.75 inch FFAR or AGR-20A APKWS II for total of 28 rockets
4 × LAU-5003 (19-Tube, CRV7 (Canadian Rocket Vehicle 7) for total of 76 rockets
4 × Digital Launcher (16 tube, R57/89 3.5 inch WAFAR (Wrap-Around Fin Aerial Rocket) or AGR-128A Angon) for a total of 64 rockets
6 × LAU-10C/A (4-tube, MK 71 5 inch ZUNI HVAR (High Velocity Aircraft Rocket) or Laser Guided Zuni) for total of 24 rockets
Missiles:
2 ×
4 × AIM-192A ATAS (Air-to-Air Scorpion) or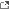 LA-430 Attero
LA-430 Attero4 × M299 Missile Launcher (4 × AGM-114K Hellfire II) for total of 16 × AGM-114K Hellfire II
4 × SPIKE-ER Helicopter Weapon System (4 × SPIKE-ER) for total of 16 × SPIKE-ER
6 × AGM-184A JSM (Joint Strike Missile)
4 × ASM/SSM-1100K Air/Ship-to-Ship Hypersonic Cruise Missile
Bombs:
24 × GBU-44/B Viper Strike w/ 1 × BAT (Brilliant Anti-Tank)
16 × 284½ lb (129 kg) "Decimator" Metric Small Diameter Gliding Bomb (MSDGB), or 250 lb (113 kg) GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb or GBU-53/B "Stormbreaker" (Small Diameter Bomb II)
8 × 551 lb (250 kg) Metric Ordnance Bomb Series,
 LAB-250 freefall general purpose gravity bomb or MK 82 LDGP (Low Drag General Purpose) 500 lb (227 kg) “Slicks” or 6 × 750 lb (340 kg) Metric Ordnance Bomb Series
LAB-250 freefall general purpose gravity bomb or MK 82 LDGP (Low Drag General Purpose) 500 lb (227 kg) “Slicks” or 6 × 750 lb (340 kg) Metric Ordnance Bomb Series6 × 750 lb (340 kg) "Pugilist" Precision Universal Gliding Bomb (PUGB) or 500 lb (227 kg) GBU-12E/B Paveway II, Paveway IV laser guided bomb, or GBU-30/B (Joint Direct Attack Munition), or BK-90/DWS 24 Mjölner w/ 72 × MJ1 (anti-personnel) or 24 × MJ2 (anti-armour) submunitions
4 × AGM-154B Joint Stand Off Weapon (JSOW) w/ 6 × BLU-108/B Sensor Fused Weapon, AGM-154C/E Block III JSOW w/ 500 lb (227 kg) BLU-111/B AUP (BROACH) warhead
Mines:
4 × 1,190½ lb (540 kg) Metric Ordnance Bomb Series DeStrucTor or 8 × 500 lb (227 kg) MK 62 Mod 0 Quickstrike or GBU-62B(V-1)/B Quickstrike-ER/MK 82 “Slicks”
Torpedoes:
8 × MK 62 Mod 0 Vortice Lightweight Torpedo, or LAIX Arms LA-92 Instigo, Schwerpunkt Arms MPLT-20 Asfirana, EuroTorp MU90 Impact, Raytheon MK 54 Mod 6 'Mako' or LIG Nex1 K745 Blue Shark
Refuelling pods: 2 × Cobham 28-300 Buddy Store Refuelling Pod (1,136 L (300 US gal) capacity w/ 833 L/m (220 gpm) offload rate)
Fuel tanks: 2 × 1,514 L (400 US gal) Sargeant Fletcher fuel tanks for increased range/loitering time
Avionics
Mission systems:
Synergy Electrodynamics AN/APQ-185 Ultra Wideband Synthetic Aperture Radar (UWBSAR)
Emerson Optronics AN/AAQ-47(V) Multi-spectral Infra-red Search and Track (MIST)
Defensive aids:
BIRD Aerosystems Airborne Missile Protection System (AMPS)
ITT Exelis AN/AAR-60(V)2 Missile Launch Detection System (MILDS-F)
Elbit Systems Multi-Spectral Infrared Countermeasure (J-MUSIC)
BAE Systems AN/ALE-47B(V)2 Countermeasures Dispenser System (CMDS)
Raytheon AN/ALR-69A(V) Radar Warning Receiver
Raytheon AN/ALQ-184 Short/Long Electronic Attack Pod
Navigation aids:
NavCom AN/APN-232 Combined Altitude Radar Altimeter (CARA)
Northrop Grumman LCR-100 Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS)
Thales Microwave And GPS Integrated Cooperative Automatic TakeOff and Landing System (MAGIC ATOLS)
Harris Airborne Sense and Avoid Radar (ABSAA)
Communications:
Rockwell Collins AN/ARC-210(V) RT-1939(C) Gen5 Programmable Digital Communication System (VHF/UHF, Joint Precision Approach and Landing System (JPALS) UHF data link, SATCOM radio)
BAE Systems AN/DPX-7 Reduced Size Transponder (RST) (Mark XIIA IFF (Mode 4/5, Mode S, TCAS II), ADS-B, TACAN, Link 16) w/ GPS Applique
Fighters | |
Strike/ground attack | |
Bombers | |
Airborne early warning | |
Command and control | |
Electronic warfare | |
Maritime patrol/sea control | |
Trainers | |
Transport | KC-16A Cargoship - MV-28A Peregrine - MV-44A Pegasus - C-75A Albatross - C-75B Super Albatross - KC-99B Majestic |
Helicopters | AH-79C Anaconda - MH-80A Barracuda - MCH-120A Pelican - CH-151A Titan Skyscrane |
Unmanned | RQ-13A Vulture - AQ-20B Renegade - RAQ-39B Clarion - MQ-45A Privateer - AQ-46A Storm Petrel - BQ-50A Dominator - MQ-59A Mosquito |













